Our providers specialize in both the surgical and nonsurgical management of Orthopaedics and sports-related condition. Most Orthopaedic and sports-related injuries and conditions can be managed non-operative (or without surgery).
The vast majority of surgeries performed at NSMI are done on an outpatient basis without admission to the hospital. Our surgeons are experts in joint preservation procedures such as arthroscopy, a minimally invasive surgery technique using a fiber optic camera inserted through small portal incisions.
Similarly, our surgeons are skilled at robotic, imaged-based computer assisted and imageless stereotactic guided surgery which ensures accurate and reproducible surgical outcomes via minimally invasive techniques.
We perform surgeries on all major joints including, but not limited to; the shoulder, elbow, hip, knee, and ankle.
Joint Preservation Procedures
When cartilage deterioration due to osteoarthritis is causing persistent joint pain that interferes with your daily life, it is our goal to restore normal movement and alleviate pain to your joint - be it your shoulder, hip, or knee. Joint preservation refers to the use of nonsurgical or surgical means to preserve a deteriorating joint in order to delay or avoid joint replacement surgery. Every patient is different, so our specialists will customize your joint preservation strategy with you based on your individual situation, taking into account factors such as your age, expectations, level of joint dysfunction, and activity level.
Arthroscopy
Arthroscopy is a surgical procedure orthopaedic surgeons use to visualize, diagnose, and treat problems inside a joint.
In an arthroscopic examination, an orthopaedic surgeon makes a small incision in the patient's skin and then inserts pencil-sized instruments that contain a small lens and lighting system to magnify and illuminate the structures inside the joint. By attaching the arthroscope to a miniature television camera, the surgeon is able to see the interior of the joint through this very small incision rather than a large incision needed for surgery.
The camera attached to the arthroscope displays the image of the joint on a computer screen, allowing the surgeon to look throughout the joint. This lets the surgeon see the cartilage, ligaments, and around the other structures of the joint. The surgeon can determine the amount or type of injury and then repair or correct the problem, if it is necessary.
We perform arthroscopies on all major joints including the shoulder, elbow, hip, knee, and ankle.
Tendon Repair
Generally, during tendon repair a surgeon will:
- make one or more small incisions (cuts) in the skin over the damaged tendon
- sew the torn ends of the tendon together
- check the surrounding tissue to make sure no other injuries have occurred, such as injury to the blood vessels or nerves
- close the incision
- cover the area with sterile bandages or dressings
- immobilize or splint the joint so as to allow the tendon to heal
Common injuries we treat with tendon repair include:
- Biceps tendon ruptures in the elbow and shoulder
- Quadricep tendon ruptures in the knee
- Patellar tendon ruptures in the knee
- Hamstring tendon ruptures in the hip
- Achilles tendon ruptures in the ankle
Tendon repairs can be very successful if they’re done along with proper physical therapy or occupational therapy. As a general rule, the sooner tendon repair surgery is done after the injury, the easier the surgery is and the easier the recovery.
Before surgery, discuss potential outcomes with your surgeon so that you have a realistic view of your individual outlook.
Ligament Repair and Reconstruction
Ligaments connect bone to bone. They help to stabilize joints at rest and during activity. When there is an injury to the ligaments, they can be stretched out or torn. This can lead to a sprain of the ligament, weakening them. In cases that are left untreated, or in cases where many sprains are experienced in a short period of time, there will be weakening of the ligaments leading to instability of the joint.

Our most common ligament procedures include but are not limited to:
- ACL reconstruction and repair in the knee
- MCL repair and reconstruction in the knee
- UCL repairs and reconstruction in the elbow
- Shoulder/labral repair and stabilization
Your provider may determine that your ligament tears or joint instability are severe enough to require surgery. The type of surgery depends on the injury to the ligaments. In some cases, ligaments can be tightened and strengthened again by placing them back onto the bone in their anatomic position, possibly using a small anchor to attach the ligaments into the bone in a ligament repair procedure.
When the ligaments are too weakened or destroyed to repair, your surgeon may recommend ligament reconstruction. Ligament reconstruction surgery involves harvesting a tendon to replace your damaged ligament.
Joint Replacement Procedures
Total joint replacement is a surgical procedure in which parts of an arthritic or damaged joint are removed and replaced with a metal, plastic or ceramic device called a prosthesis. The prosthesis is designed to replicate the movement of a normal, healthy joint. Hip and knee replacements are the most commonly performed joint replacements, but replacement surgery can be performed on other joints, as well, including the ankle, wrist, shoulder, and elbow.
Here at NSMI, we specialize in Knee and Shoulder replacements. For patient who require other joint replacements we are happy to help to coordinate your care with the right surgeon.
Total Knee Arthroplasty
If nonsurgical treatments like weight loss, physical therapy, injections, bracing, medications and using walking supports are no longer helpful, you may be a candidate for a total knee replacement surgery.
Joint replacement surgery is a safe and effective procedure to relieve pain, correct leg deformity, and help you resume normal activities.
Most people who have total knee replacement surgery experience a dramatic reduction of knee pain and a significant improvement in the ability to perform common activities of daily living. But total knee replacement will not allow you to do more than you could before you developed arthritis.

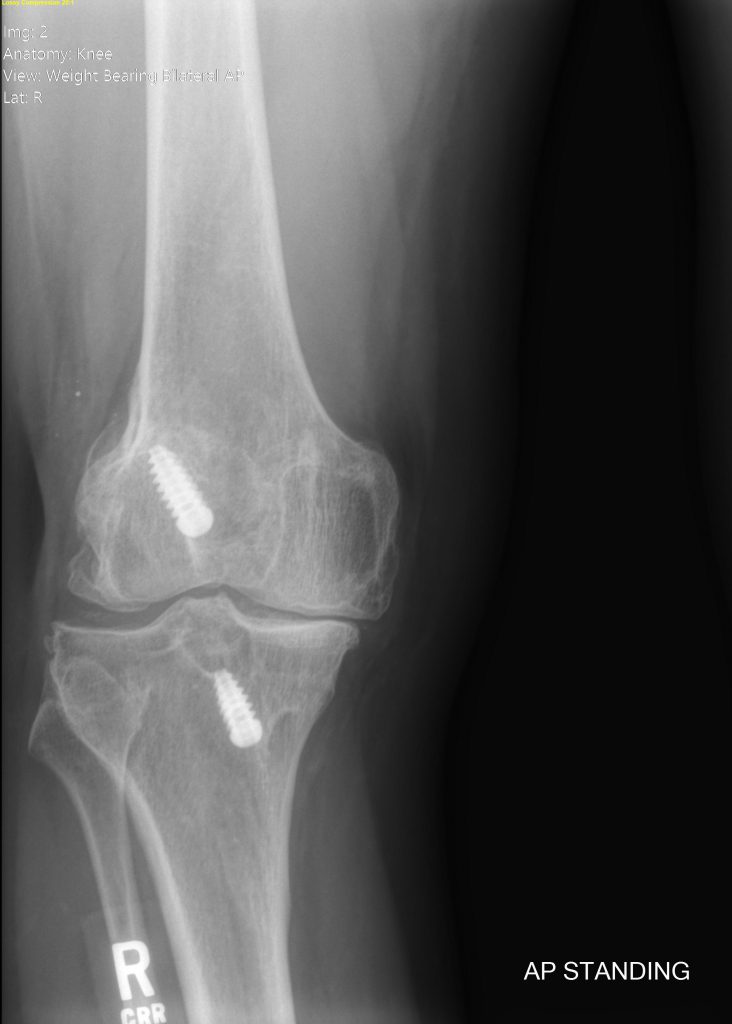
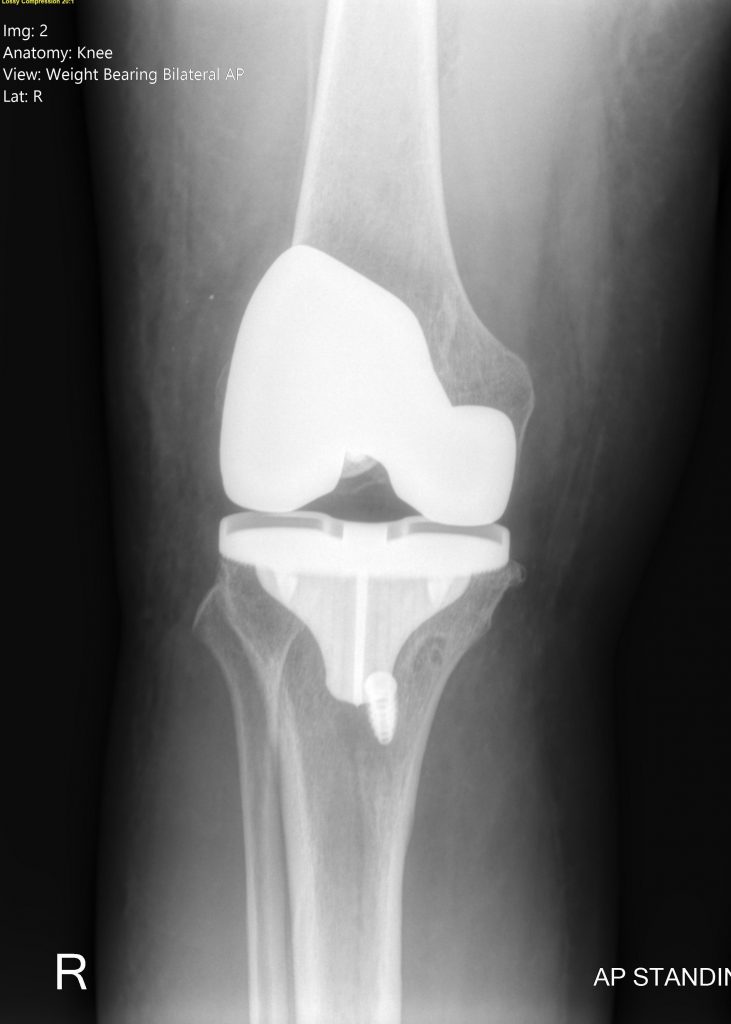
With normal use and activity, every knee replacement implant begins to wear in its plastic spacer. Excessive activity or weight may speed up this normal wear and may cause the knee replacement to loosen and become painful.
Realistic activities following total knee replacement include unlimited walking, swimming, golf, driving, light hiking, biking, ballroom dancing, and other low-impact sports.
With appropriate activity modification, knee replacements can last for many years.
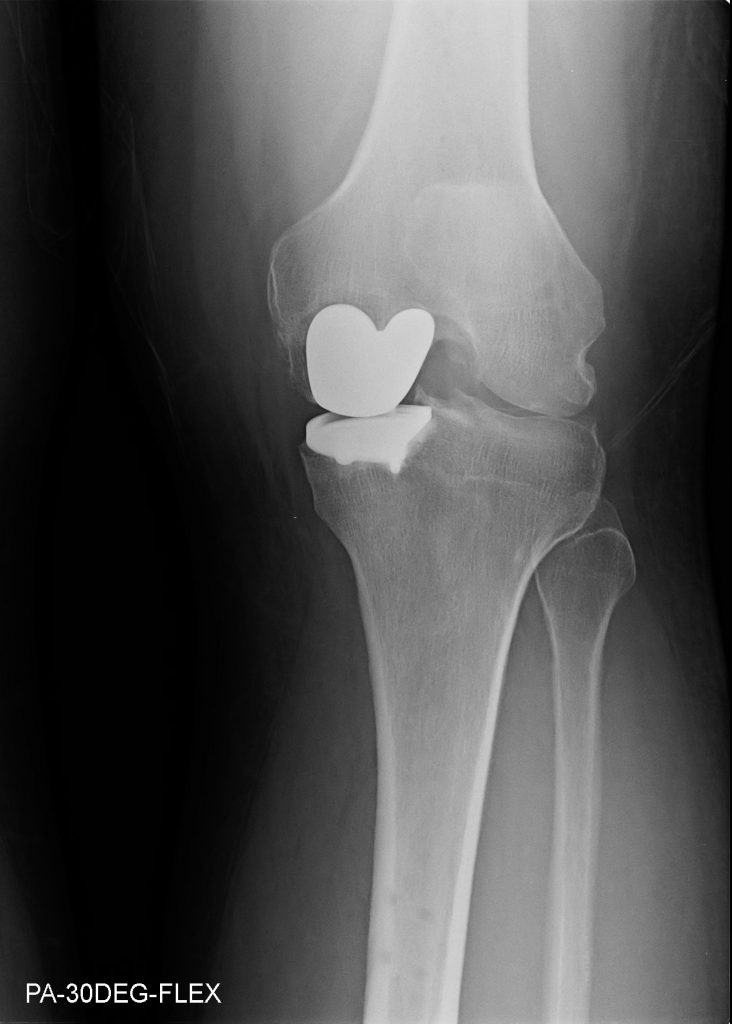
Partial (Unicompartmental) Knee Arthroplasty
During knee replacement surgery, damaged bone and cartilage is resurfaced with metal and plastic components. In unicompartmental knee replacement (also called "partial" knee replacement) only a portion of the knee is resurfaced. This procedure is an alternative to total knee replacement for patients whose disease is limited to just one area of the knee.
Because a partial knee replacement is done through a smaller incision, patients usually spend less time in the hospital and return to normal activities sooner than total knee replacement patients.
There are a range of treatments for knee osteoarthritis and your provider will discuss with you the options that will best relieve your individual osteoarthritis symptoms.
Total Shoulder Arthroplasty and Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty
Although shoulder joint replacement is less common than knee or hip replacement, it is just as successful in relieving joint pain.
If nonsurgical treatments like medications, activity changes, physical therapy, bracing, and injections are no longer helpful for relieving pain, you may be a candidate for a total shoulder joint replacement surgery. Joint replacement surgery is a safe and effective procedure to relieve pain and help you resume everyday activities.
Every year, thousands of conventional total shoulder replacements are successfully done in the United States for patients with shoulder arthritis. This type of surgery, however, is not as beneficial for patients with large rotator cuff tears who have developed a complex type of shoulder arthritis called "cuff tear arthropathy." For these patients, conventional total shoulder replacement may result in pain and limited motion, and reverse total shoulder replacement is a better option.
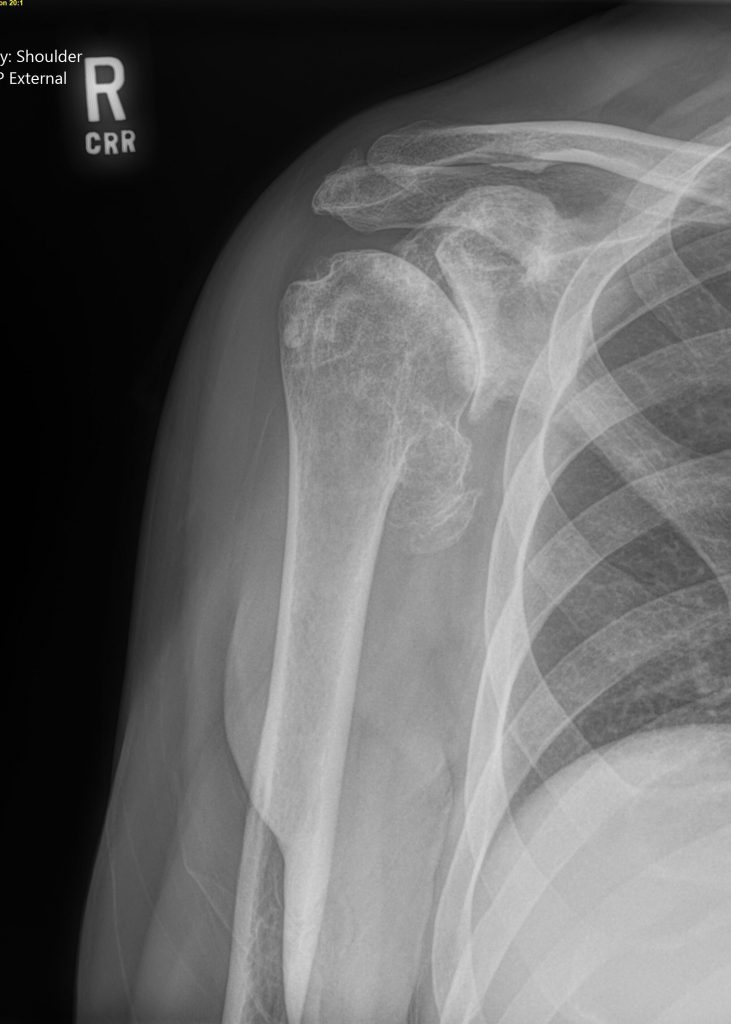
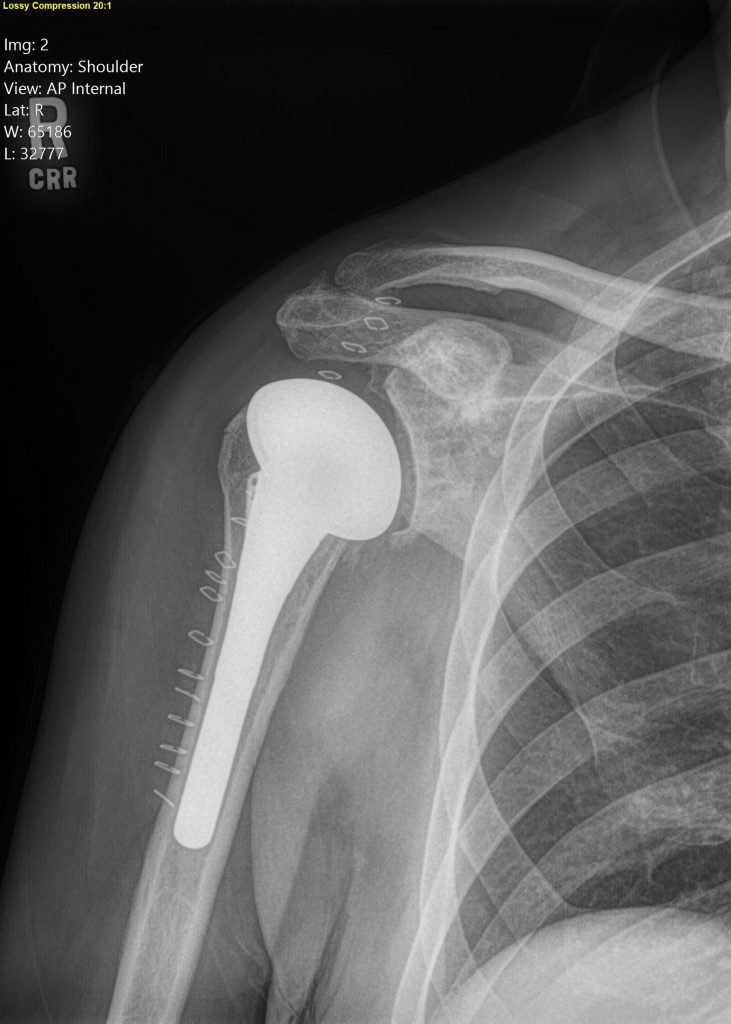

There are a range of treatments for shoulder osteoarthritis and your provider will discuss with you the options that will best relieve your individual osteoarthritis symptoms.

